The Gnu Data Language is an interactive interpreter/incremental compiler for the GNU Data Language, which is primarily used in scientific, astronomical, medical and geo-science data processing applications. It supports graphical output and is intentionally designed to be highly compatible with the commercial IDL language. GDL is a free IDL (Interactive Data Language) compatible incremental compiler (ie. runs IDL programs). For a list of functions / compatability try this list.
After installation and choosing an editor it is time to delve in to some code. In the “Beginner Code Examples” below, I am the beginner so no questions about programming please!
Example 1 – Command Line
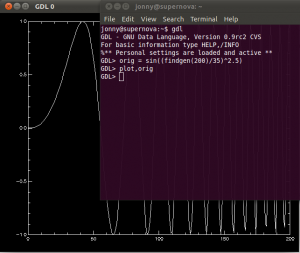
Open a terminal (e.g. Applications > Accessories > Terminal ) and start GDL with command gdl on the command line.
A simple plot is displayed with the following GDL commands:
GDL> orig = sin((findgen(200)/35)^2.5)
GDL> plot,orig
GDL> exit
Example 2
GDL> a=2
GDL> b=a*2
GDL> print, b
4
Example 3
In this example we are first going to get an image file from Wikipedia to use in our example, then create a .pro file using a simple text editor and finally compile and run the .pro file:
sudo mkdir -p /usr/examples/data cd /home/jonny/gdl wget http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/c/c8/Lunar-eclipse-09-11-2003.jpeg sudo mv Lunar-eclipse-09-11-2003.jpeg /usr/examples/data/moon.jpg
gedit get_image.pro
PRO get_image
file = filepath('moon.jpg', subdir=['examples','data'])
read_jpeg, file, image
window, xsize=500, ysize=500
device, decomposed=0
loadct, 25
tvscl, image
END
jonny@nova$ gdl
GDL> .COMPILE get_image.pro
% Compiled module: GET_IMAGE.
GDL> get_image
A window should be displayed possibly not displaying much of the moon image but I don’t yet know the purpose of loadct except that it accepts values from 0 to 40 so you could try a few of these to see what they do – I’m on the steeper end of a learning curve here.
Example 3
It is also possible to run .pro files in batch mode without compiling. Just omit the .pro extension and prefix with the @ symbol:
GDL> @get_image
Example 4
vi circle_area.pro area = !DPI * 24 ^ 2 print, area
Now at the bash command line try:
gdl < circle_area.pro | grep -v “^%”
Here we are feeding the .pro file into GDL and grepping to remove (-v) any lines beginning(^) with the % sign to avoid getting lines like:
% Compiled module: LOADCT
Potential Pitfalls
Not all IDL functionality is available yet in GDL. For example, I had issues with the following:
- % Function not found: QUERY_IMAGE – I could not get my example code to use this function: Query_image
- Function not found: DIALOG_PICKFILE – The function for a GUI to choose a file. I couldn’t find this so it is possibly not part of GDL.
- GDLFFDICOM__ASSOC::ASSOC: No pixeldata tag found – I received this error when trying to read a dicom file I was given e.g. dicom_obj -> Read(‘Sagittal_slice’) . However, when I used a dicom image downloaded online it worked fine. Possibly some header metadata missing on this dicom image?
- Installing GDL an IDL alternative
- GDL Editors on Linux
- GDL: Beginner Code Examples
- GDL: Taking It Further
QUERY_IMAGE and DIALOG_PICKFILE are available since years in GDL.
I would advocate *not* to use FILEPATH since it is really IDL & PATH dependent
You have to use TV, image, /true
for images in the form [3, xsize, ysize]
Don’t hesitate to provide the Dicom file with problem.