Ensure the deb repo is configured and install nomad:
curl -fsSL https://apt.releases.hashicorp.com/gpg | sudo apt-key add -
sudo apt-add-repository "deb [arch=amd64] https://apt.releases.hashicorp.com $(lsb_release -cs) main"
sudo apt-get update && sudo apt-get install nomadEnvironment Variables
export NOMAD_ADDR=http://192.168.1.91:4646Development Mode
These commands are for testing non-production tasks. In this example I am running on a server with IP address 192.168.1.91
nomad agent -dev -bind 192.168.1.91 -log-level INFOThe web UI will be available on that IP port 4646
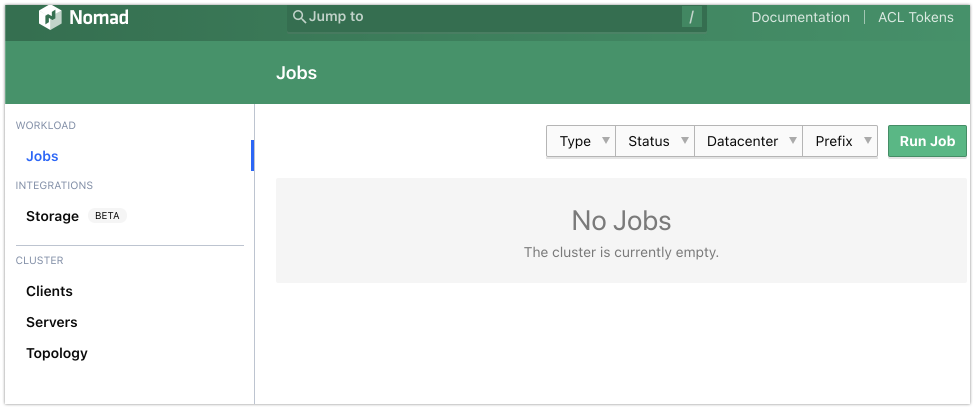
Check the status of the node:
nomad node status
nomad server membersID DC Name Class Drain Eligibility Status
3829cafc dc1 consul-1011 <none> false eligible readyRunning a test redis job
nomad job init
nomad job run example.nomadThe init produces a deployment configuration as shown below. The run task runs that job and can be seen in the UI and CLI status commands.
job "example" {
datacenters = ["dc1"]
type = "service"
update {
max_parallel = 1
min_healthy_time = "10s"
healthy_deadline = "3m"
progress_deadline = "10m"
auto_revert = false
canary = 0
}
migrate {
max_parallel = 1
health_check = "checks"
min_healthy_time = "10s"
healthy_deadline = "5m"
}
group "cache" {
count = 1
network {
port "db" {
to = 6379
}
}
service {
name = "redis-cache"
tags = ["global", "cache"]
port = "db"
}
restart {
attempts = 2
interval = "30m"
delay = "15s"
mode = "fail"
}
ephemeral_disk {
size = 300
}
task "redis" {
driver = "docker"
config {
image = "redis:3.2"
ports = ["db"]
}
resources {
}
}
}
}
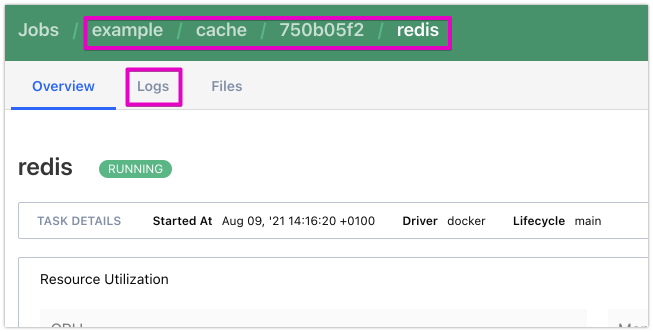
You can drill down through the Job, Allocation, Task and logs with:
nomad job status example
nomad alloc status 750b05f2
nomad alloc logs 750b05f2 redisWithin the UI you can do the same. The breadcrumb shows the hierarchy of job, group, allocation, job:
Next step is to run Nomad servers with a config file that defines the cluster and agents that will be managed by that cluster.