Like a virtual machine for running a version of Android, the Android emulator is useful for testing. I used it to check how websites looked under Android.
After installing the Android SDK run the ./android binary in the ‘tools’ directory and install some versions of Android.
Then from the menu bar choose Tools > Manage AVDs > New …
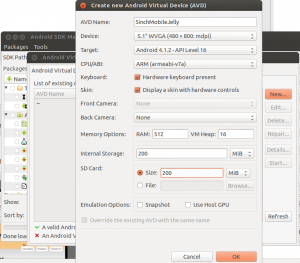
Create the new AVD
Then back at the command line run the ./emulator binary in the ‘tools’ directory with the name of the AVD you created i.e.
./emulator -avd 5inchMobileJelly
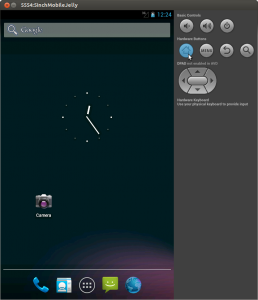
Gotchas:
- It may be necessary to chmod +x ./android ./emulator* to make sure all the binaries in the tools directory are executable.
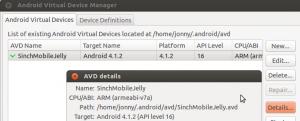
- You can find the location of where your AVD is stored on disk by clicking the Details button when managing AVDs